amyloid beta plaque|What Happens to the Brain in Alzheimer's Disease? : Tuguegarao The beta-amyloid 42 form is thought to be especially toxic. In the Alzheimer’s brain, abnormal levels of this naturally occurring protein clump together to form plaques that disrupt cell function. 139 subscribers ‧ 20 videos. Official YouTube channel for Triple Nine.
amyloid beta plaque,
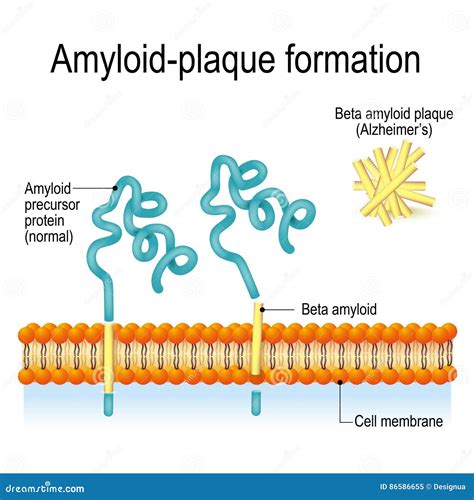
Amyloid plaques (also known as neuritic plaques, amyloid beta plaques or senile plaques) are extracellular deposits of amyloid beta (Aβ) protein that present mainly in the grey matter of the brain. [1][2][3][4] Degenerative neuronal elements and an abundance of microglia and astrocytes can be associated with amyloid plaques.Aβ plaques are one of the two lesions in the brain that define the neuropathological diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Plaques are highly diverse structures; many of them include massed, fibrillar polymers of the Aβ protein referred to as A β -amyloid, but some lack the defining features of .
amyloid beta plaque JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — Mayo Clinic researchers led a laboratory study that found a new way to prevent the accumulation of amyloid plaque – a key feature of Alzheimer’s disease – by eliminating a class of molecules called heparan sulfates that form on brain cells.amyloid beta plaque What Happens to the Brain in Alzheimer's Disease? JACKSONVILLE, Fla. — Mayo Clinic researchers led a laboratory study that found a new way to prevent the accumulation of amyloid plaque – a key feature of Alzheimer’s disease – by eliminating a class of molecules called heparan sulfates that form on brain cells.

The beta-amyloid 42 form is thought to be especially toxic. In the Alzheimer’s brain, abnormal levels of this naturally occurring protein clump together to form plaques that disrupt cell function.

The beta-amyloid 42 form is thought to be especially toxic. In the Alzheimer’s brain, abnormal levels of this naturally occurring protein clump together to form plaques that disrupt cell function.
Breakthroughs in molecular medicine have positioned the amyloid-β (Aβ) pathway at the center of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) pathophysiology.
Beta-amyloid plaque accumulates in the brain of people with Alzheimer’s disease and other forms of dementia. These icky little clumps stick together outside the brain’s nerve . The production and deposition of the amyloid beta peptide appear to play a central role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease and form the basis of the amyloid cascade hypothesis. Amyloid plaques are easily visible on routine hematoxylin and .
What Happens to the Brain in Alzheimer's Disease?In AD, the dysregulation of the amyloid-beta (Aβ) level leads to the appearance of senile plaques which contain Aβ depositions. Aβ is a complex biological molecule which interacts with many types of receptors and/or forms insoluble assemblies and, eventually, its nonphysiological depositions alternate with the normal neuronal conditions.
amyloid beta plaque|What Happens to the Brain in Alzheimer's Disease?
PH0 · Why Does Beta
PH1 · What are Amyloid Plaques?
PH2 · What Happens to the Brain in Alzheimer's Disease?
PH3 · The Amyloid
PH4 · Mayo Clinic Researchers Find Way to Prevent Accumulation of Amyloid
PH5 · Is Beta
PH6 · Aβ plaques
PH7 · Amyloid plaques
PH8 · Amyloid Beta Peptide
PH9 · Amyloid